Blog Sep. 19, 2019
A 5G Future: Its Impact on Mobile Application Developers

Mobile communications are about to enter a new frontier. With the development of 5G technology, users and businesses alike have more opportunities to look forward to. Experts have forecasted that 5G will pave the way to the Fourth Industrial Revolution where 5G networks and devices will be “used to enable wireless remote control and coordination of production from a distance”(*). The introduction of new technologies and standards are a turning point in the progress or decline of numerous industries, including mobile app development.
Since 5G is set to become one of the world’s most significant and transformative technologies, mobile app developers would greatly benefit from learning more about this new network. Read on for an overview of 5G, the history of its development, and its benefits and disadvantages for mobile app developers.
* See: Decoding 5G: A cheat sheet for next-gen cellular concepts and jargon / Venture Beat
What is 5G?
Set for a global launch in 2020, 5G is the latest generation of wireless technology. It is anticipated as one of the fastest, most robust technologies in existence. This technology promises quicker downloads and excellent network reliability. With 5G, upload and download speeds will become exponentially faster. In addition, latency – the time it takes for devices to transfer data through wireless networks – will also decrease considerably (What is 5G? / Verizon). 5G involves utilizing a higher frequency in the radio spectrum, thus increasing the bandwidth for data transmission. A wider bandwidth allows significantly more devices to access the wireless network simultaneously (What are 5G frequency bands / RF Page). These improvements in connectivity will enable businesses to increase efficiency and provide consumers access to more information faster, resulting in a substantial impact on modern life (What is 5G and what will it mean for you? / BBC).
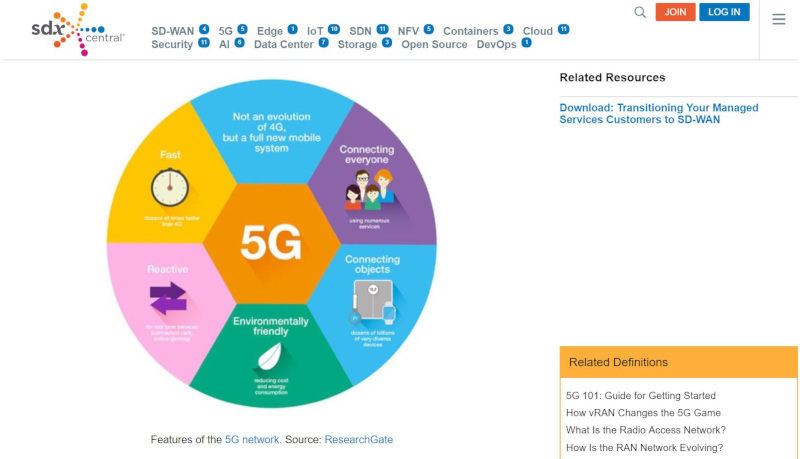
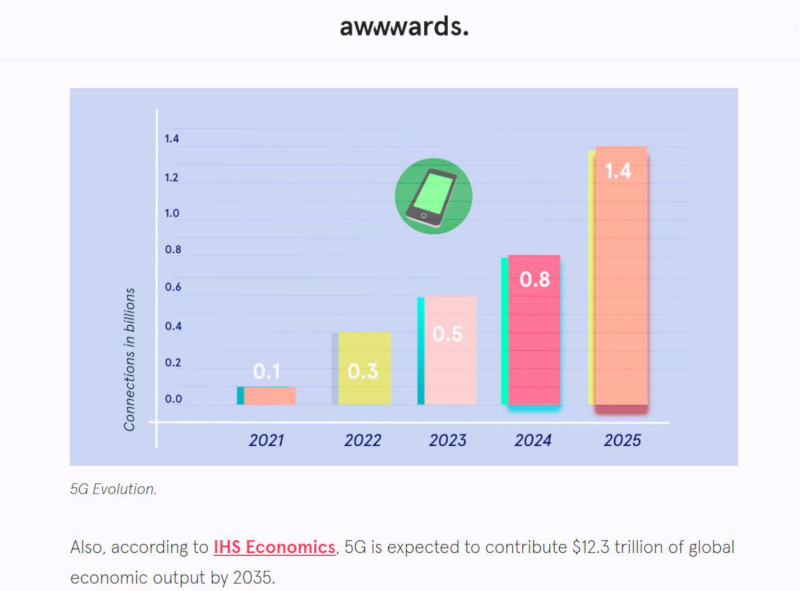
According to a study conducted by the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA), 5G is estimated to reach 1.4 billion connections, accounting for 15% of mobile connections across the globe by 2025. The study further reveals that 16 major markets worldwide will greenlight commercial 5G networks in 2019, following the initial launches in the United States and South Korea in 2018 (New GSMA Study: 5G to Account for 15% of Global Mobile Industry by 2025 as 5G Network Launches Accelerate / GSMA). Additionally, research by Information Handling Services (IHS) Economics indicates that 5G is anticipated to contribute $12.3 trillion of global economic output by 2035 (The 5G economy: How 5G technology will contribute to the global economy / IHS Economics). These figures provide a clear insight of the substantial influence that the introduction of 5G will bring to the economy, and its effect on daily lives all over the world.
Rise of 5G
“5G” stands for the fifth generation of wireless technology. Typically, every generation has been defined by its data transmission speeds. However, the differences in generations does not stop there. Each step forward also introduced distinct changes to wireless technology (The 5G Revolution / The Economist). Becoming familiar with the predecessors of 5G is key to understanding its impact on mobile app developers.
1G
The first generation of wireless communications, now dubbed as “1G,” was developed in the late 1970s, with standards established and fully implemented through the 1980s. It was initially launched by the Nippon Telephone and Telegraph Company (NTT) in Japan during 1979. Categorized as analog technology, 1G allowed people to make voice-only calls between mobile phones. The maximum data transfer speed of 1G technology was roughly 2.4 kilobits per second (kbps). However, devices using 1G had poor voice quality and battery life, less security than its successors, and limited cell coverage (Evolution of wireless technologies 1G to 5G in mobile communication / RF Page).
2G
A decade after 1G, wireless technology received its first major upgrade in the form of 2G, which successfully turned cell phones from analog to digital. Developed in Finland, 2G introduced numerous fundamental cell phone services that are still in place today, such as Short Message Service (SMS), Internet access facilities, international roaming, conference calls, and usage-based billing. This technology had a maximum data transfer speed of 50kbps (1G Vs. 2G Vs. 3G Vs. 4G Vs. 5G / Net-informations.com).
Furthermore, 2G introduced the Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), which became the basis of further developments in wireless standards. Consequently, the Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) system developed by Qualcomm was launched during the mid-1990s. CDMA increased the bandwidth efficiency, the user capacity, and data transfer rate (Evolution of wireless technologies 1G to 5G in mobile communication / RF Page).
3G
Launched commercially in 2001, 3G utilizes the Universal Mobile Terrestrial / Telecommunication System (UMTS) as its core network structure. This network integrated features of the 2G network with newer technology and protocols to provide a considerably higher data rate. As such, the data transfer rate for 3G was at least 200kbps and could theoretically reach up to 21.6 megabits per second (Mbps). Moreover, this technology ushered in the smartphone revolution where web browsing, email, picture sharing, multimedia chat, video calling, games, social media, and healthcare on mobile devices became possible (1G Vs. 2G Vs. 3G Vs. 4G Vs. 5G / Net-informations.com).
4G
4G, the current standard of wireless communications, was developed in 2008. A massive leap from 3G, this technology provided a maximum real-world data transfer speed of 100Mbps, enabling users to engage in data-intensive activities such as online gaming, video conferencing, cloud computing, and high-definition live media streaming (1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, & 5G Explained / LifeWire).
5G
Now, the newest generation of wireless mobile communications is about to emerge. 5G not only provides the features of its predecessors but also provides three unique aspects to wireless communication.
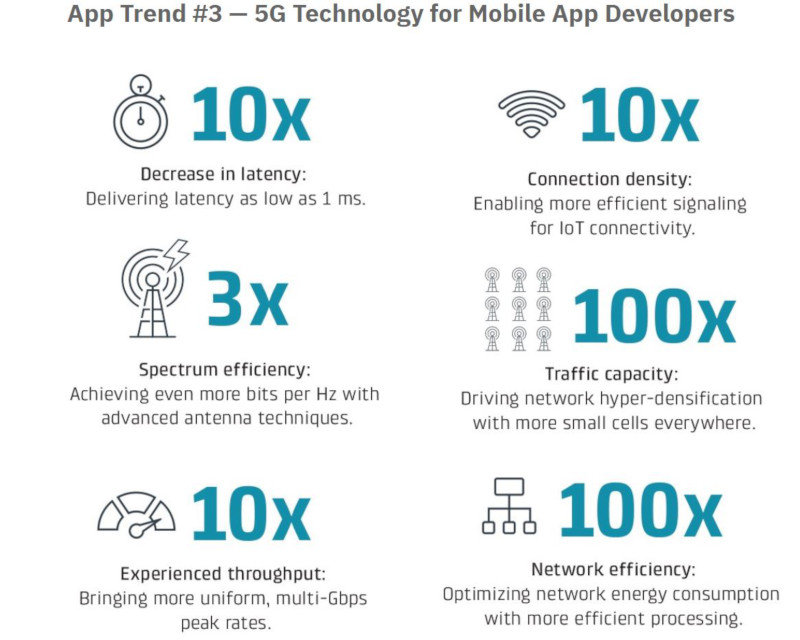
First, it delivers a much faster data transfer of at least one gigabit per second (1Gbps) and up to 50Gbps, having even reached approximately one terabit per second (1Tbps) in some test environments. Nevertheless, 5G is expected to provide a consistent data transfer speed of 2.8Gbps in the real-world environment, which is a big step up from the speed of 60Mbps of 4G (How Fast is 5G? / 5GUK Limited).
Second, it provides a lower latency of merely one millisecond, compared to 4G’s average latency of 50 milliseconds. Third, it offers a higher capacity to connect more devices simultaneously. Unlike 4G, which permits only 60,680 devices to connect within one square kilometer, 5G allows the connection of up to 1 million devices in the same area (5G and Massive IoT: legacy technologies will bridge the gap for now / IHS Markit). These radical changes in wireless connectivity will open doors for several industries, most notably in mobile app development.
The Benefits of 5G for Mobile Application Developers
With the emergence of the 5G network, mobile connectivity will be quicker and better than ever. This technological progress will result in extreme changes in the mobile app development industry, especially in smoother and more efficient mobile app performance. Here are some of the opportunities that developers can look forward to:
Faster file transfers
With 5G’s fastest file transfer speed, apps that revolve on the transfer of data, files, money, or anything transferable between devices will gain an excellent advantage (How will 5G Networks Impact Mobile Apps in 2019-2020? / AppInventiv). For example, users of video streaming apps will be able to enjoy lag-free viewing of 4K and 360° videos from their smart devices (How 5G Will Change the Mobile App Development Landscape / Awwwards).
Media-rich User Experiences
The clarity of User Interfaces (UI) will be one of the significant benefits resulting from 5G technology. Developers will be able to improve the UI of their apps, since the performance of any customer servicing app relies heavily on UI. This can provide developers a considerable competitive edge to their product (How 5G Network will change Mobile App Development Scenario? / TechAhead).
Better features and greater capacity
Due to the 5G network’s near-instant speed and lower latency, developers will be more open to integrating additional features and capacities to devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) and augmented or virtual reality apps (AR/VR). This leads to more possibilities in providing powerful and extraordinary user experiences. Such improvements can benefit developers in increasing user retention as well as overall app revenues (How 5G Will Change the Mobile App Development Landscape / Awwwards).
Next-level navigation apps
A door to a whole new world of opportunities in the development of GPS-enabled mobile apps will be opened as a result of 5G’s high-quality and uninterrupted capabilities. Apps for travel and tourism, as well as those for utilities and wearables, will most likely benefit from 5G’s ability to handle more data and connect more devices simultaneously (What the Coming of 5G Means for Mobile App Development? / Thinksys). For instance, 5G could help lessen road congestion by allowing stoplights to change based on real-time traffic patterns. Moreover, 5G could be the stepping stone for the development of automatic driving, as it will improve efficiency and the reliability of self-driving vehicles (How 5G Could Transform the Travel Industry / The Points Guy).
Cutting-edge 3D models
Mobile app development involved in 3D gaming and immersive augmented reality (AR) will also gain a substantial advantage with the emergence of 5G, due to its rapid data transfer and near-zero network latency. AR apps will grow more sophisticated leading to improved shared and social real-time AR experiences. For example, AR-enhanced live events could be made possible with 5G (How 5G could improve augmented reality / TechRadar). Additionally, the marriage of 5G-enabled mobile apps with innovative 3D printers will allow users to produce high-quality 3D models of objects. Such apps will be useful in a broad range of industries, from construction to healthcare (How 5G Network will change Mobile App Development Scenario? / TechAhead).
Improved Customer Support
Even though Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology behind chatbots may not yet be fully capable of replacing human counterparts, connecting chatbots through the 5G network can be beneficial; bound to create opportunities for prompt and real-time feedback. Shorter wait times mean improved exchanges, which may hugely benefit apps that provide customer support using chat. (What the Coming of 5G Means for Mobile App Development? / Thinksys).
Decreasing hardware dependency
5G will provide lightning-speed, real-time connections between devices, where gigabytes of data can be transferred with little to no delay. As a result, a mobile app’s performance will rely less on the device hardware’s processing power since data centers will be doing the bulk of the processing. This may well-lay the groundwork for device-agnostic apps. (How 5G Will Change the Mobile App Development Landscape / Awwwards).
The Disadvantages of 5G for Mobile Application Developers
In spite of the many benefits of 5G technology, some issues may be unavoidable for developers.
The following are some examples of the disadvantages that developers might experience.
Privacy and security risks
5G’s greater speed and higher capacity for connected devices and networks may result in some major loopholes in privacy and security. Given that more data of various kinds would be transmitted across 5G networks, much of these might contain sensitive information that hackers could take advantage of for nefarious purposes.
Additionally, the increased dependency on the mobile network also poses a great risk because its disruption would result in dire consequences in safety and economic activity. For example, a failure during a remotely controlled operation could result in a crash of a self-driving vehicle or even the death of a patient. (5G: a revolution not without risks / ABS-CBN).
The Need for a 5G-based Business Model
The present business model that developers use is designed for 4G technology. As such, this business model may prove to be insufficient in fully unleashing the potential that the speed of a 5G network would bring. This could prove to be a great challenge for mobile application strategists (How 5G Will Change the Mobile App Development Landscape / Awwwards).
Multiple App Versions
Although consumers are expected to start using 5G-enabled devices upon the implementation of 5G, other devices would still be running on 2G, 3G, or 4G networks. Developers will then have to take on the challenge of creating multiple app versions to cater to all their users with different devices (How 5G Network will change Mobile App Development Scenario? / TechAhead).
With all these benefits and disadvantages the 5G revolution brings about, there are endless possibilities in mobile app development. Developers’ success will rely on how they will adjust to these industry changes.
Preparing for the 5G revolution
The pursuit of better communication has led to the continuous development of wireless technology, from the analog 1G to the subsequent digital generations. There is no doubt that 5G technology will prove to be a game-changer in the arena of mobile app development due to its incredible speed, near-zero network latency, and greater bandwidth.
However, 5G brings both benefits and disadvantages to mobile app developers. On the one hand, the benefits of 5G come in forms of faster file transfer, media-rich user experiences, better features and greater capacities, next-level navigation apps, cutting-edge 3D models, improved customer support, and decreased hardware dependency. On the other hand, the disadvantages that app developers might experience include privacy and security risks, the need for a 5G-based business model, and multiple app versions. As such, adjustment to the impact of 5G will prove to be crucial for an app developer’s success.
For developers who value the preparation for 5G networks, but have qualms about reallocating internal resources that may already be spread thin, why not partner with an experienced customer support expert like adish to outsource some tasks? Since 2010, adish Co., Ltd. has provided multilingual online services in customer support, monitoring, and community management. We have the expertise to help developers with customer support as they pursue improvement in preparation for the 5G revolution.